 Lawyer & Corina, 2014
Lawyer & Corina, 2014
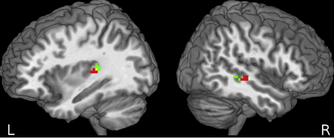
fMRI
With the fMRI method, changes in blood flow as a function of experimental tasks can be measured. fMRI is used to examine neural circuits involved in language processing, and to assess how language networks interact with other cognitive networks in the brain.
With the fMRI method, changes in blood flow as a function of experimental tasks can be measured. fMRI is used to examine neural circuits involved in language processing, and to assess how language networks interact with other cognitive networks in the brain.
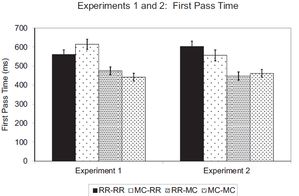
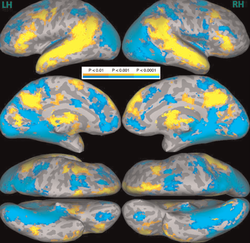 Choi & Henderson, 2015
Choi & Henderson, 2015
Combined Eyetracking and fMRI
Eye-movements during reading have been considered a source of movement artifacts in studies of reading comprehension. Many studies of reading using the fMRI method have therefore presented sentences and texts one-word-at-a-time via RSVP (Rapid Serial Visual Presentation), thereby preventing natural reading processes.
The Henderson Lab combines functional Imaging with on-line eyetracking during reading of text to better understand brain circuits involved in language processing under natural reading conditions.
Eye-movements during reading have been considered a source of movement artifacts in studies of reading comprehension. Many studies of reading using the fMRI method have therefore presented sentences and texts one-word-at-a-time via RSVP (Rapid Serial Visual Presentation), thereby preventing natural reading processes.
The Henderson Lab combines functional Imaging with on-line eyetracking during reading of text to better understand brain circuits involved in language processing under natural reading conditions.
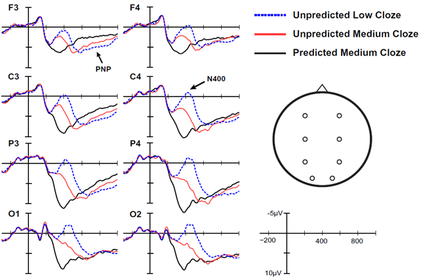
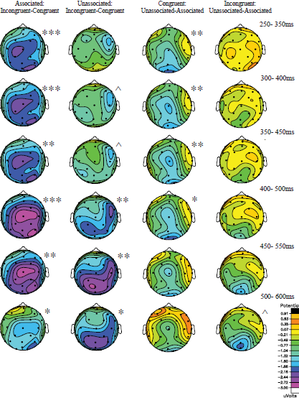
Event-Related Potentials (ERPs)
The ERP method provides a sensitive neural measure of language processes as it unfolds in real time during reading and listening comprehension and production. With this method we can identify multiple neurocognitive processes because a given behavior is often accompanied by multiple ERP effects. Reliable ERPs can be measured without a behavioral task, allowing for covert monitoring of behavior. This is useful, for example, in studies of sentence and discourse comprehension, because processing can be measured at multiple instances without task-interruption, or when testing patient populations.
The ERP method provides a sensitive neural measure of language processes as it unfolds in real time during reading and listening comprehension and production. With this method we can identify multiple neurocognitive processes because a given behavior is often accompanied by multiple ERP effects. Reliable ERPs can be measured without a behavioral task, allowing for covert monitoring of behavior. This is useful, for example, in studies of sentence and discourse comprehension, because processing can be measured at multiple instances without task-interruption, or when testing patient populations.